TABLE OF CONTENTS |
mini-examples |
|
|
Mini Example #1 - A 1 Dimensional Closed "Sloshing" BasinThis example is a simplified, 1 dimensional case of a closed basin. The basin contains some level of water initially, a pulse of water or hydrograph is forced in from the left edge, and then the left edge is immediately closed, leaving the wave to travel back and forth in the closed basin.
Click here for a video of the simulation (48 secs.)
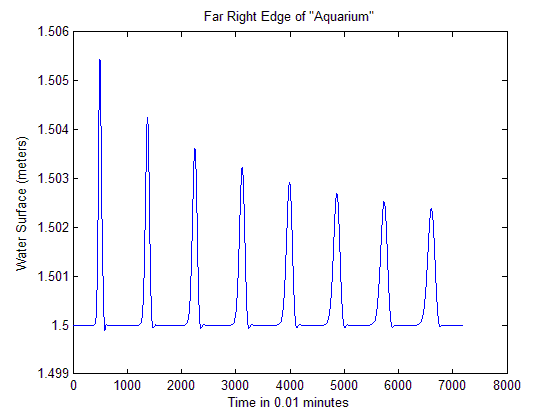
This is the right edge of the basin Note in the figure above, there is a delay from the instant the pulse of water was forced in and the time it took to travel to the other end of the basin. From the above figure, it can also be concluded that the travel time for the wave to go from one edge to the other and back is about 9 minutes. To cover a distance of 2000 meters in 9 minutes, the wave speed would have to be 3.7 m/s. Using the shallow water approximation, where C = sqrt(g*d), the velocity comes out to be 3.8 m/s. These results are very close and give confidence in the models performance.
This shows the velocity near the left boundary Note in the figure above, the velocity near the boundary shows times of negative velocity when the wave is traveling towards the boundary (moving right to left), and positive velocity soon after when the wave has reflected off of the NO FLOW boundary and is moving from left to right again.
Mini Example #2 - A 2 Dimensional Drop in a BucketThis example is a simplified 2-D case where a flat, still water surface is laid out. At an instant in time, the middle of the surface is displaced by 0.25 meters downward, imitating the instant something, such as a pebble, is dropped on the surface. The water surface is then free to equilibrate.
Click here for a video of the simulation (7 secs.)
Water Surface of the center cell of square grid Note in the above figure that the center cell is disturbed initially and then rebounds. This rebounding decays over time as the surface quiets.
Water surface of a boundary cell
|