
Estuaries are unique coastal regions where a river meets a large open body of water. Recent studies show that changing climate can dramatically affect the flow dynamics and ecosystems of estuaries. For example, observed global mean sea levels have risen steadily over the past century and are projected to increase into the future. These changes in downstream water levels affect the slope of estuarine rivers, yielding a shift in discharge patterns. In addition, episodes of heavy precipitation show upward trends and global climate models predict tropical storm rainfall will increase under a changing climate, creating abnormal estuary discharge. While the importance of changing climate in estuaries is recognized, our ability to quantify riverine or estuarine discharge during extreme precipitation events like typhoons or thunderstorms is hindered by a lack of reliable and sustainable measurement techniques.
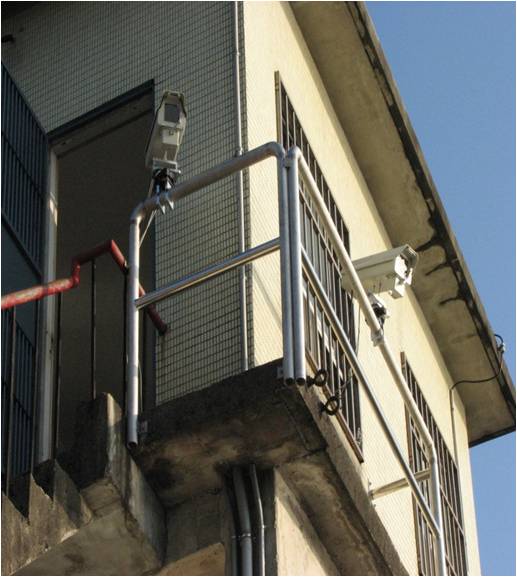
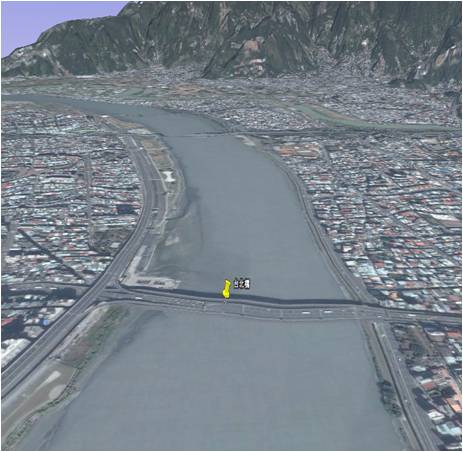


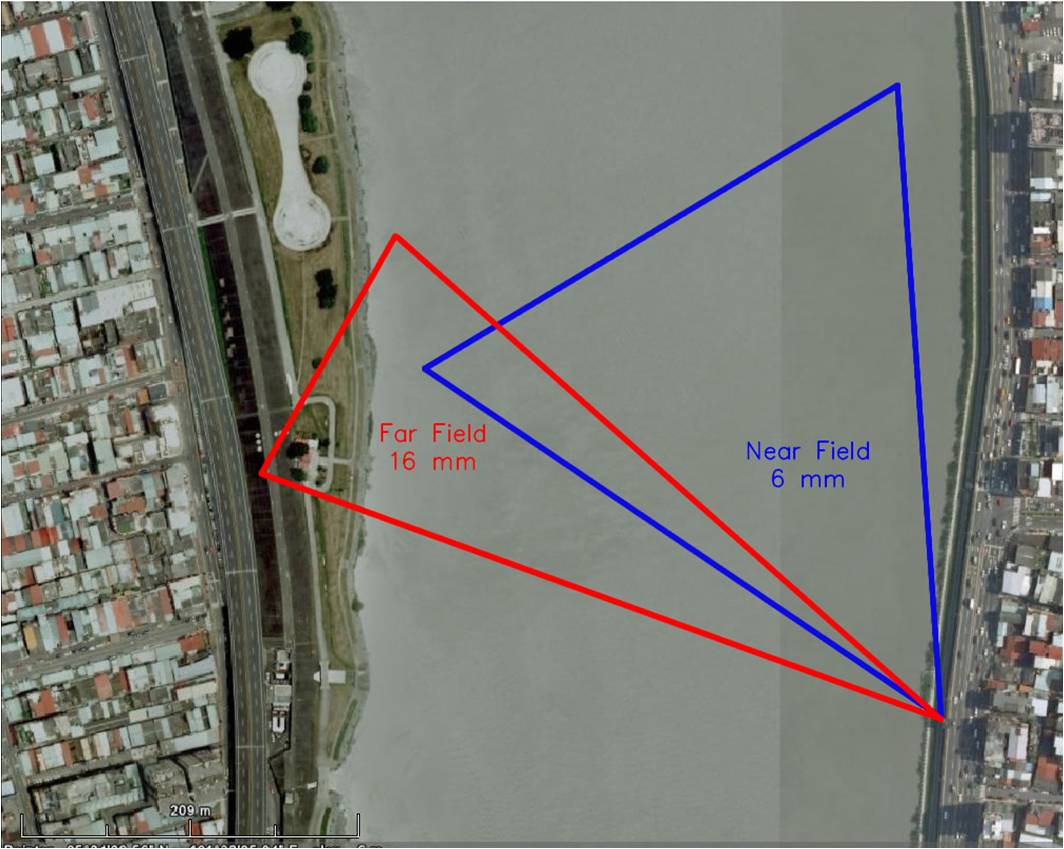
(a) AREDIS on the Danshui River in Taiwan. (b) The length of the river cross section is 400 m. (c) AREDIS dual-camera system for far- and near-field
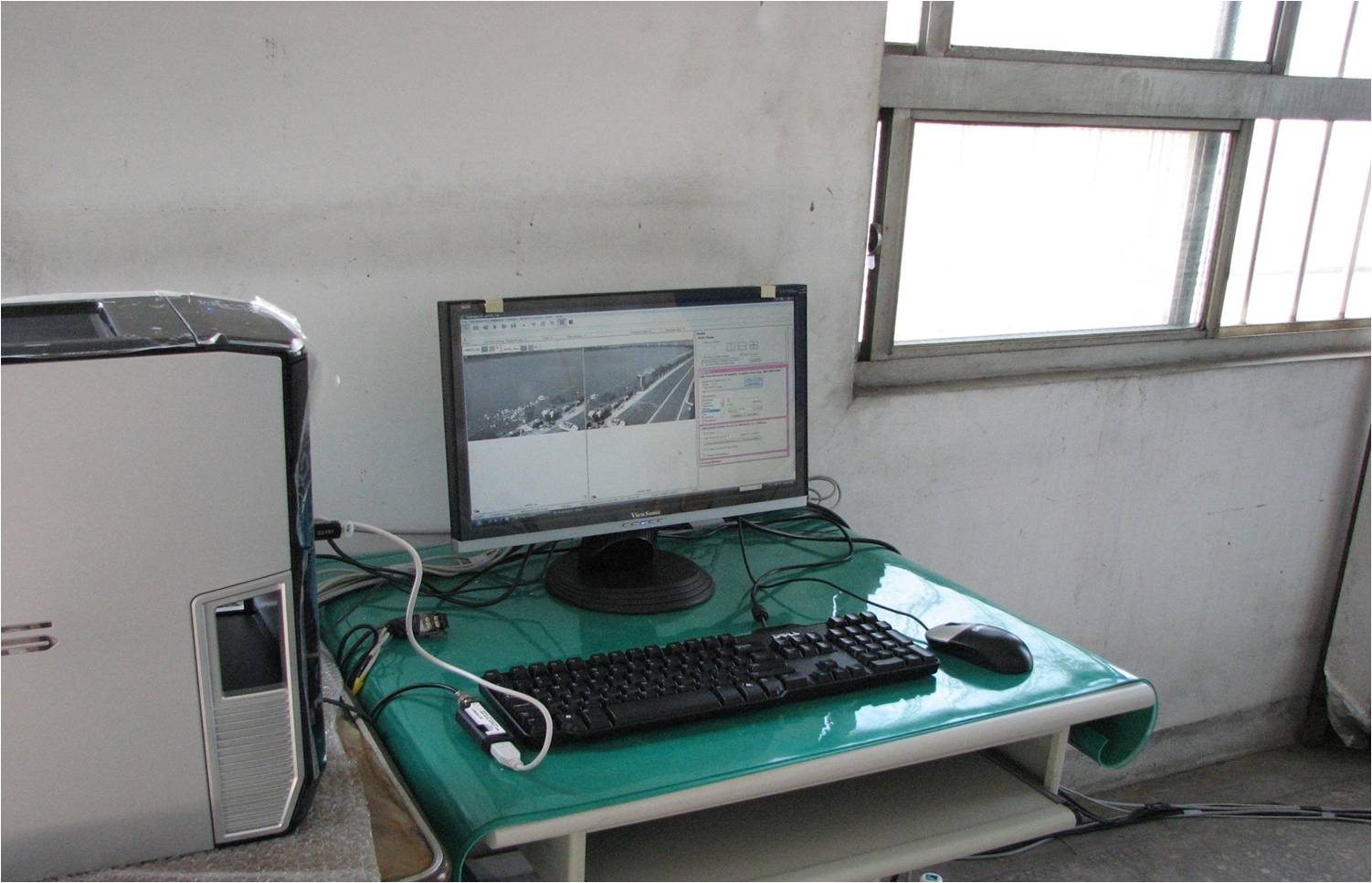
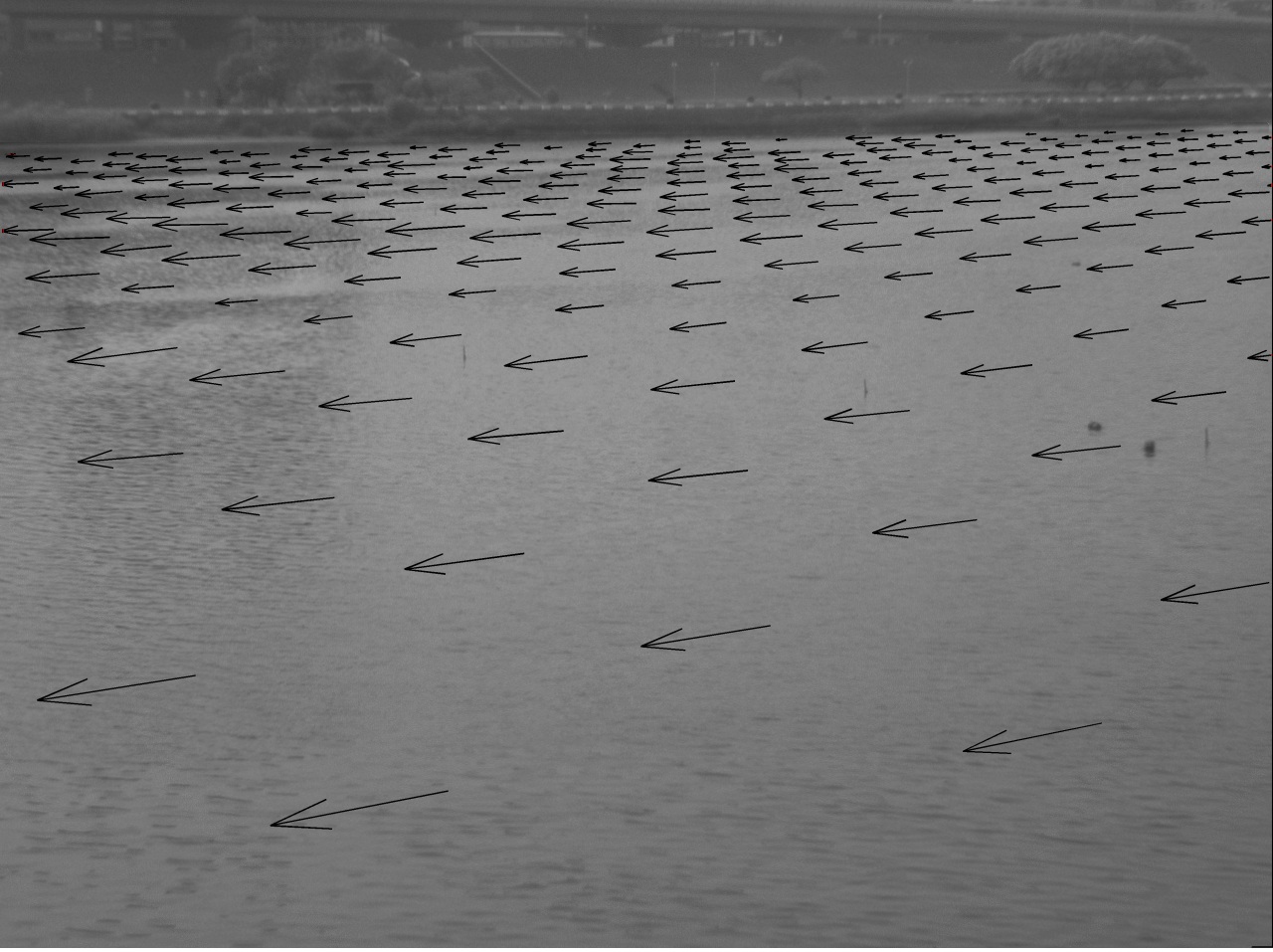
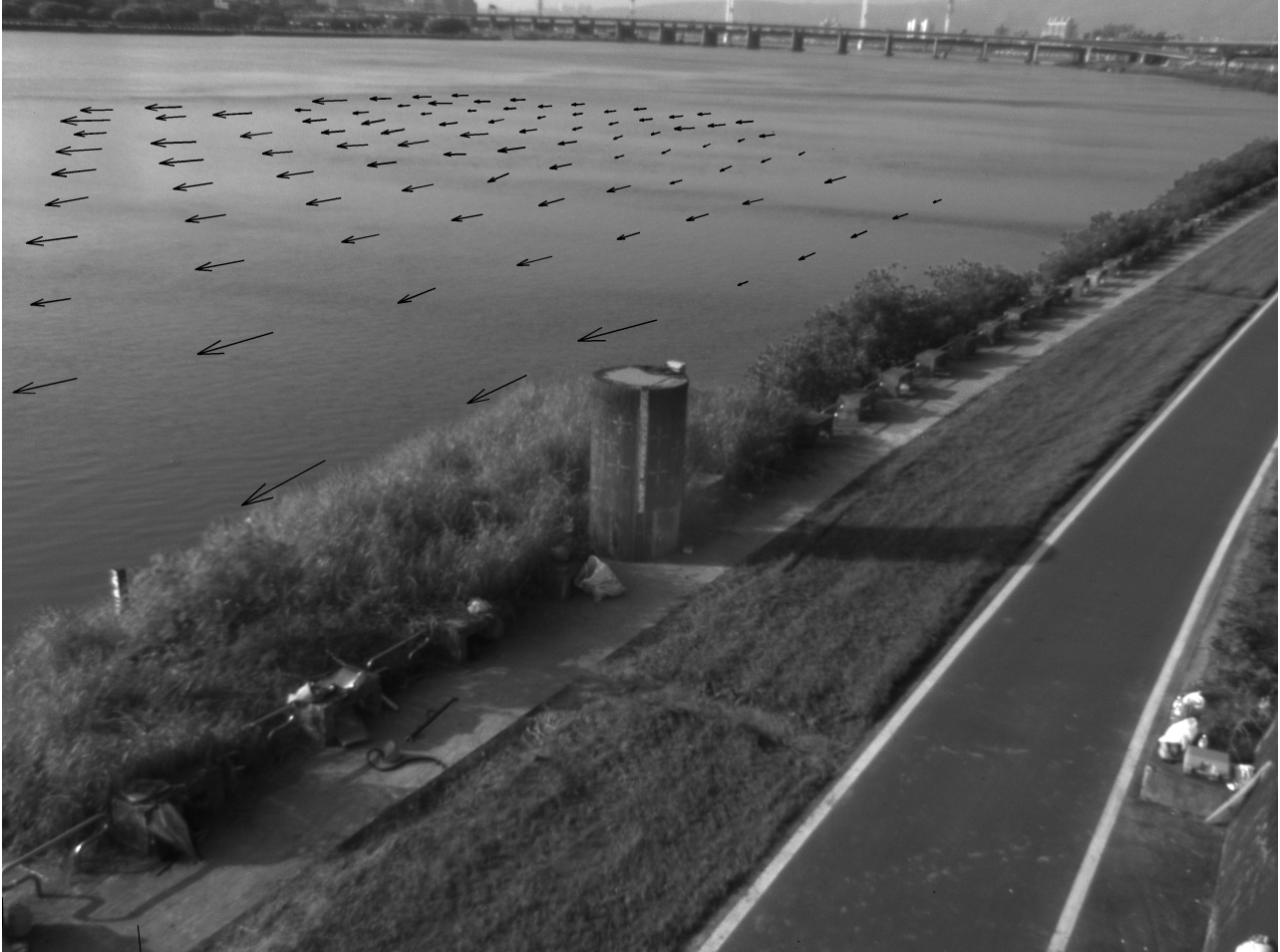



(d) AREDIS Remote Graphical User Interface (e) Large-Scale PIV (LSPIV) for far-field view (f) LSPIV for near-field view
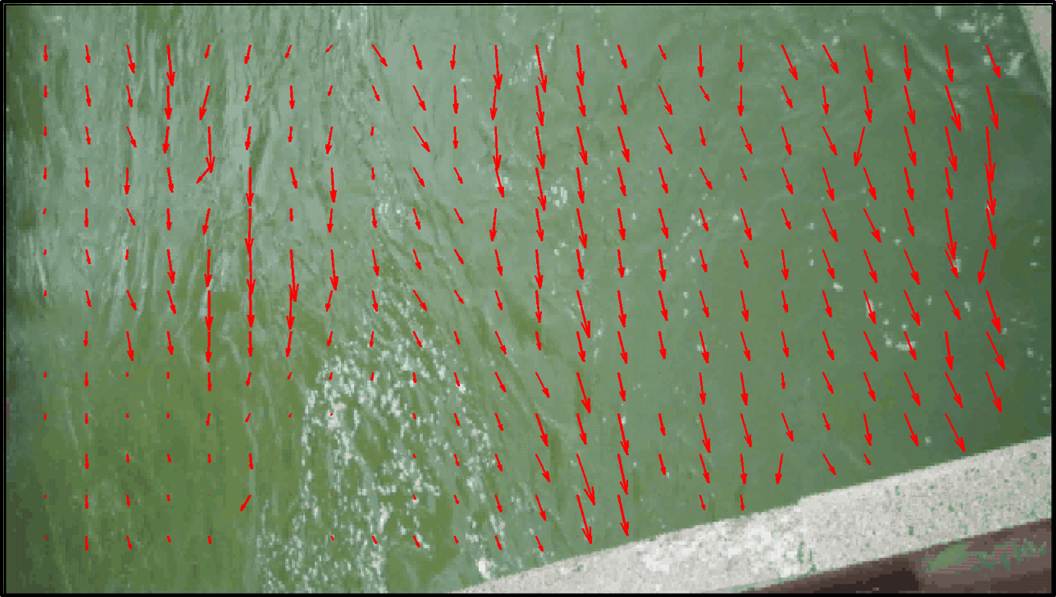
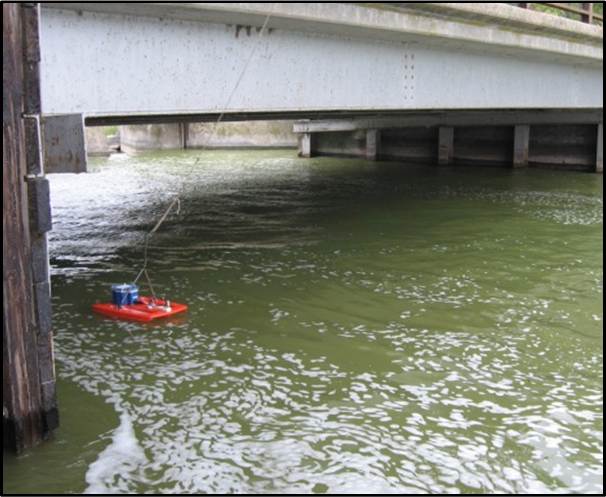



(e) AREDIS2 at Lafollette Dam, Yahara River, WI (f) LSPIV for non-uniform surface velocity (g) Discharged measured by a moving ADCP
Sponsor :
Dane County Land and Water Resources Department
NSF
Water Resources Agency MOEA, Taiwan
Wisconsin Hilldale Faculty/Undergraduate Research Fellowships
Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation
Status : Active
Student Investigators:
Yuli Liu (PhD), John Reimer (PhD)
Graduated: Adam Bechle (PhD), Nobuaki Kimura (PhD), Wei-Bo Chen (PhD), W.C. Huang (MS), William Kasch (MS).
Collaborators: Professor Wen-Cheng Liu
Dr. Nobuaki Kimura
Publications
- Liu, Y, Bechle, A.J., and Wu, C.H., A Unified
Wide-Angle Oblique Automated Streamflow Imaging System
(UW-OASIS) for Discharge Measurement near Hydraulic
Structures, to be submitted.
- Liu, Y., Wu, C.H., Reimer, J.R.. An adaptive
entropy-based discharge estimate for short-term water
fluctuations, to be submitted, 2017.
- Bechle, A.J. and Wu, C.H. An entropy-based surface velocity method for estuarine discharge measurement, Water Resources Research, DOI:10.1002/2014WR015353, 2014.
- Bechle, A.J., Wu, C.H., Liu, W.C., and Kimura, N.,
Development and Application of an Automated
River-Estuary Discharge Imaging System, J. of
Hydraulic Engineering-ASCE, 138(4), 327-339, 2012.
- Kimura, N.. Liu, W.C., Wu, C.H., Bechle, A.J., Chen, W.B.,and Huang, W.C., Flow measurement with multi-instrumentation in a tidal affected river, Water and Environment Journal, 25(4), 563-572, 2011.
- Liu, W.C., Chen, W.B., and Wu, C.H., Modelling effects of realignment of Keeling River, Taiwan. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers Maritime Engineering, 161, MA2, 73-97, 2008.
- Liu, W.C., Chen, W.B., Kuo, J.T., and Wu, C.H., Numerical determination of residence time and age in a partially mixed estuary using three-dimensional hydrodynamic model, Continental Shelf Research, 28(8), 1068-1088, 2008.
- Water Resources Agency MOEA, Final Report, Development
of an Automated River Discharge Imaging System (ARDIS)
in high discharge flows. 2008.